In our increasingly connected world, voice-controlled virtual assistants such as Amazon Alexa have become an integral part of our daily lives. These artificial intelligence-enabled assistants offer convenience and ease of use by enabling users to interact with various web services through natural language dialogs. However, as the popularity of virtual assistants grows, so do concerns about privacy and data security.
Hey APOCRAT, give me an overview
In this blog article, we take a closer look at the Alexa Skill Ecosystem, going over the research that was done in the paper "Hey Alexa, is this Skill Safe? Taking a Closer Look at the Alexa Skill Ecosystem." If you want to get a better understanding of the topic before reading this article, here is the video with the summary by one of the authors.
The results of the study shed light on the limitations and potential risks associated with third-party applications, known as Alexa Skills. While these Skills extend Alexa's functionality by offering a wide range of services, they also raise legitimate privacy and data protection concerns for users.
By the end of this article, you will gain a deeper understanding of the privacy concerns within the Alexa skill ecosystem and the importance of consent management in protecting your personal data. Join us on this journey as we explore the delicate balance between the convenience of voice-controlled virtual assistants and the critical need for privacy in a constantly connected world.
Transparency Challenges in Skill Activation
The study identifies a lack of transparency in how Amazon auto-enables skills with duplicate invocation names. This can result in users inadvertently activating the wrong skill. Although there is a positive correlation between skill activation and the number of ratings received, it does not imply causation. Auto-enabled skills appearing on users' companion apps make it easier for them to provide ratings, potentially leading to misleading feedback.
Vulnerabilities in Skill Publishing
The research reveals that attackers can publish skills using well-known company names, exploiting the absence of automated infringement detection for third-party trademarks. Amazon's reliance on manual vetting makes it prone to human error. Consequently, users may be exposed to phishing attacks launched by malicious actors.
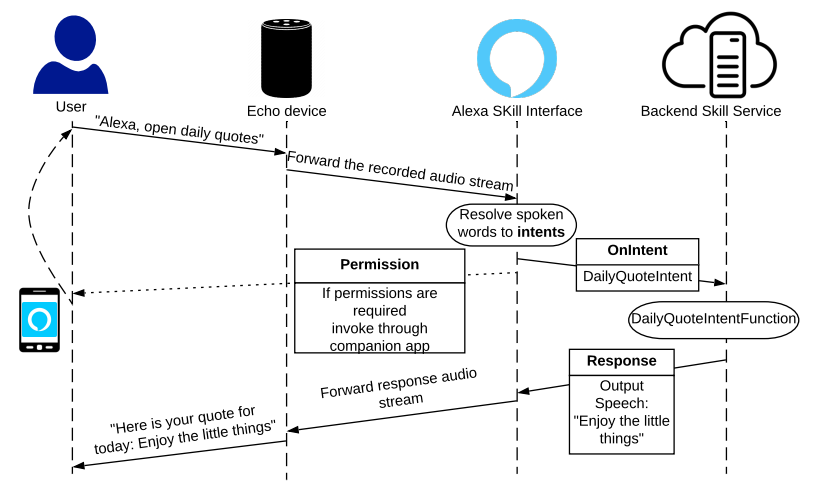
Alexa skill workflow from "Hey Alexa, is this Skill Safe? Taking a Closer Look at the Alexa Skill Ecosystem"
Manipulating Skills to Reveal Sensitive Data
The study highlights that attackers can make code changes to approved skills, coercing users into divulging sensitive information. During the certification process, attackers can register dormant intents that are never triggered, evading suspicion. Subsequently, after certification, they modify the backend code to trigger dormant intents, potentially compromising user data.
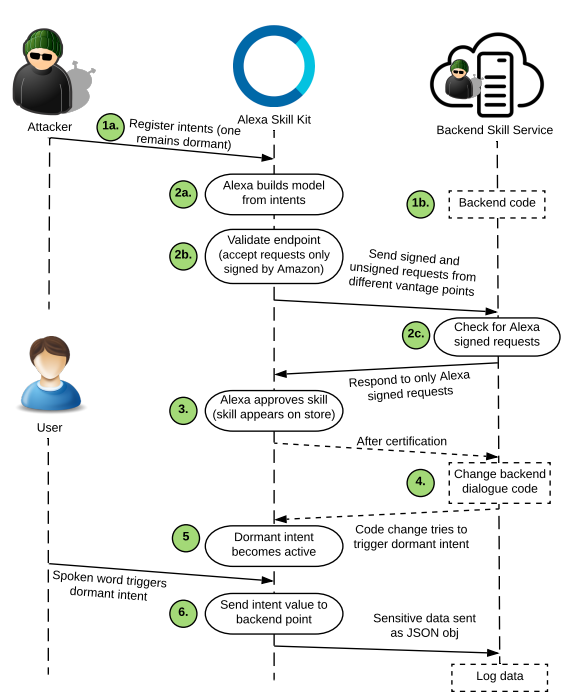
Attack on Skills froms "Hey Alexa, is this Skill Safe? Taking a Closer Look at the Alexa Skill Ecosystem"
Inadequate Protection of Sensitive Data
The paper uncovers flaws in Alexa's mediation of sensitive data types. Attackers can directly request permission-protected data types, bypassing the intended safeguards. Even when attackers use built-in data types, such as Amazon.Phone, skills requesting sensitive data do not get flagged appropriately. This conceptual flaw hinders users' understanding of who is collecting their data, blurring the distinction between native and third-party skills.
Evaluation of Skill Squatting Patterns
Although the study identifies different skill squatting patterns, it does not find evidence of systematic malicious abuse in the real world. However, this non-detection may be attributed to mitigation strategies employed by Amazon, influenced by prior research. Nonetheless, understanding these squatting approaches is crucial for mitigating potential risks.
Factors Influencing Skill Squatting Success
Certain approaches within each skill squatting pattern have a higher likelihood of successfully squatting skills. Correct/accepted spelling increases the chances of launching the expected skill, while alterations in punctuation decrease activation rates. Word-spacing also plays a role, with joint words succeeding more frequently.
Privacy Policies in Skill Categories
The study highlights the prevalence of privacy policies in different skill categories. Only 13.6% of skills in the 'kids' category provide a privacy policy, despite the potential for stricter controls and the need for safeguarding children's privacy. Similarly, skills in the 'health and fitness' category show a somewhat higher prevalence of privacy policies at 42.2%. As privacy advocates, we believe that both 'kid' and 'health' related skills should adhere to higher standards when it comes to data privacy. It's important to note that the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) closely monitors skills in the 'kids' category for potential violations of the Children's Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA), emphasizing the significance of stricter controls in these domains. This topic remains highly relevant and this press statement by the FTC only emphasizes its importance.
Evaluation of Privacy Policy Links
The research reveals that 90% of skills in the US requesting permissions provide a valid privacy policy. However, approximately 10% of policy links lead to page not found errors, server issues, or unregistered domains. Interestingly, some skills (30 in total) direct users to unrelated websites' homepages, highlighting inconsistencies in privacy policy adherence.
Gaps in Data Type Disclosure
Around 23.3% of privacy policies fail to fully disclose the data types associated with the permissions requested by the skill. Notably, a significant portion of skills (33.1%) accessing the Full Name permission does not disclose the collection of such data in their privacy policies, potentially raising concerns about data usage and user awareness.
Herausforderungen bei Vorlagen für Datenschutzrichtlinien
The study identifies potential regulatory non-compliance in 46 skills due to privacy policy templates. Developers often rely on these templates, resulting in inconsistencies between requested permissions and policy disclosures. This highlights a fundamental flaw in the current publishing model of app markets, where developers have access to users' personally identifiable information (PII) without sufficient guidance to create proper privacy policies. Ultimately, this lack of transparency places the burden of privacy risks on end-users.
In line with APOCRAT's mission, these findings are consistent with our commitment to empowering users and protecting their privacy. By understanding the risks and implementing effective consent management strategies, we can improve user control and ensure the responsible use of personal data in the IoT landscape.
Contact
Partner & Sales Manager: Alexander Jürgens
E-Mail: office@apocrat.at
Mobile: +43 676 4025255

